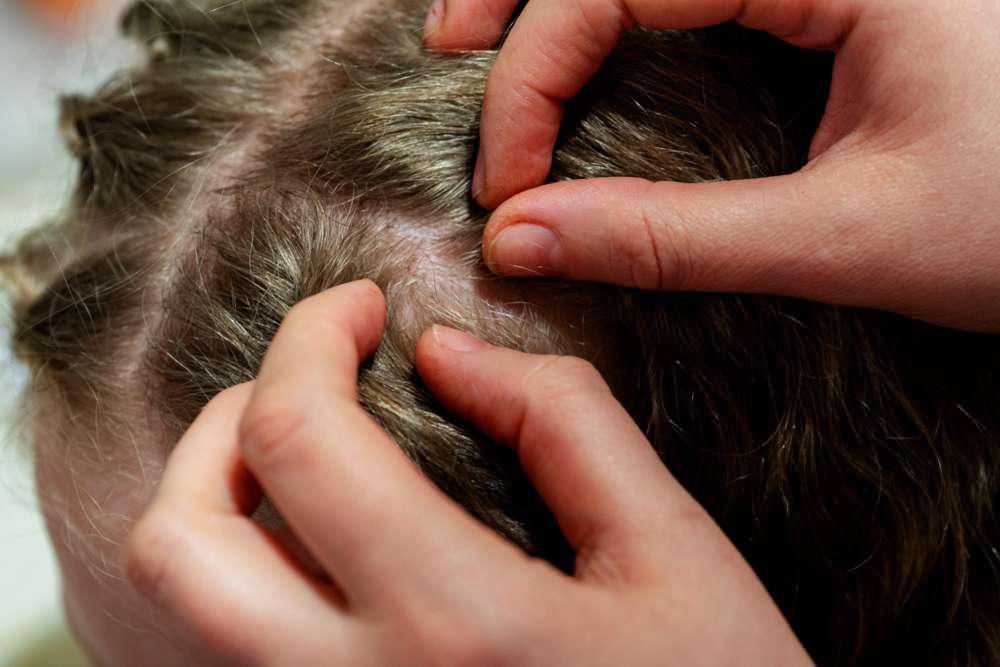
Understanding the Risks: Why Seniors Shouldn’t Ignore Atopic Dermatitis Symptoms
Atopic dermatitis, commonly known as eczema, affects individuals of all ages — but its impact on older adults can often be underestimated. For seniors, symptoms like chronic itching, dry patches, and skin sensitivity can lead to more than just discomfort. These issues may interfere with sleep, increase infection risks, or worsen pre-existing health conditions. This article explores why it’s essential for seniors to recognize the early signs of atopic dermatitis and seek timely support from healthcare professionals. Awareness and proactive care can significantly improve quality of life.
What are the common symptoms of atopic dermatitis in seniors?
Atopic dermatitis in seniors often presents differently than in younger individuals. Common symptoms include dry, scaly skin that may appear thickened or leathery due to long-term inflammation. Seniors may experience intense itching, particularly at night, which can disrupt sleep patterns. Redness and inflammation are typical, especially in skin folds like the elbows, behind the knees, and on the neck. Unlike younger patients, older adults might have more generalized skin involvement, with symptoms appearing on larger areas of the body, including the face and hands.
How does atopic dermatitis uniquely impact older adults?
The impact of atopic dermatitis on seniors extends beyond skin discomfort. Older adults often have thinner, more fragile skin that’s prone to tearing and slower to heal. This increased vulnerability can lead to a higher risk of secondary bacterial infections when scratching occurs. Moreover, the chronic nature of atopic dermatitis can exacerbate other age-related health issues. Sleep disturbances caused by persistent itching may lead to daytime fatigue, increased fall risk, and cognitive impairment. The visible symptoms can also affect self-esteem and social interactions, potentially leading to isolation and depression in some seniors.
What are the early warning signs of eczema seniors should watch for?
Recognizing the early warning signs of atopic dermatitis is crucial for prompt intervention. Seniors should be alert to any persistent dry, itchy patches of skin, even if they’re small. Increased skin sensitivity, especially to certain fabrics or skincare products, can be an early indicator. Subtle changes in skin texture, such as roughness or scaliness, particularly in areas like the hands, face, or neck, should not be ignored. Seniors might also notice that their skin feels tighter or less elastic than usual. Any new or worsening patches of redness, especially those that don’t resolve quickly, warrant attention.
What strategies can seniors use to manage skin irritation and dryness?
Managing skin irritation and dryness is key to controlling atopic dermatitis symptoms in seniors. A gentle skincare routine is essential, using fragrance-free, hypoallergenic products specifically designed for sensitive skin. Regular moisturizing, particularly after bathing while the skin is still damp, helps lock in hydration. Seniors should opt for lukewarm water when bathing and limit shower or bath time to prevent further drying of the skin. Humidifiers can be beneficial, especially in dry climates or during winter months when indoor heating can deplete skin moisture. Wearing soft, breathable fabrics and avoiding known irritants can also help reduce flare-ups.
When should seniors seek medical attention for persistent skin issues?
Seniors should not hesitate to seek medical attention if they experience persistent or worsening skin issues. It’s important to consult a healthcare professional if itching becomes severe enough to interfere with daily activities or sleep. Any signs of infection, such as increased redness, warmth, swelling, or the presence of pus, require prompt medical evaluation. If over-the-counter treatments fail to provide relief after a few weeks, or if new areas of the body become affected, it’s time to see a doctor. Additionally, seniors with pre-existing health conditions should be particularly vigilant, as atopic dermatitis can sometimes interact with or exacerbate other medical issues.
What treatment options are available for seniors with atopic dermatitis?
Treatment options for atopic dermatitis in seniors are tailored to individual needs and the severity of symptoms. Topical corticosteroids are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and itching, but they must be used cautiously in older adults due to potential side effects on thinning skin. Non-steroidal topical immunomodulators, such as tacrolimus or pimecrolimus, can be effective alternatives. For more severe cases, oral medications or phototherapy might be recommended. Antihistamines can help manage itching, especially at night. It’s crucial for seniors to work closely with their healthcare providers to find the right balance of treatments, considering potential interactions with other medications and age-related factors.
When considering treatment options, it’s important to understand the associated costs, as they can vary significantly depending on the type and duration of treatment. Here’s a comparison of some common treatment options for atopic dermatitis in seniors:
| Treatment Option | Provider Type | Estimated Cost Range |
|---|---|---|
| Topical Corticosteroids | Prescription (Pharmacy) | $10 - $50 per tube |
| Tacrolimus/Pimecrolimus | Prescription (Pharmacy) | $100 - $300 per tube |
| Oral Antihistamines | Over-the-counter/Prescription | $5 - $30 per month |
| Phototherapy | Dermatology Clinic | $100 - $300 per session |
| Oral Immunosuppressants | Prescription (Pharmacy) | $50 - $500 per month |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
In conclusion, atopic dermatitis in seniors is a condition that requires attention and proactive management. By recognizing early symptoms, implementing proper skincare routines, and seeking timely medical intervention, older adults can effectively manage their condition and maintain a good quality of life. It’s crucial for seniors and their caregivers to stay informed about the unique challenges atopic dermatitis presents in older populations and to work closely with healthcare providers to develop personalized treatment plans.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.
The shared information of this article is up-to-date as of the publishing date. For more up-to-date information, please conduct your own research.