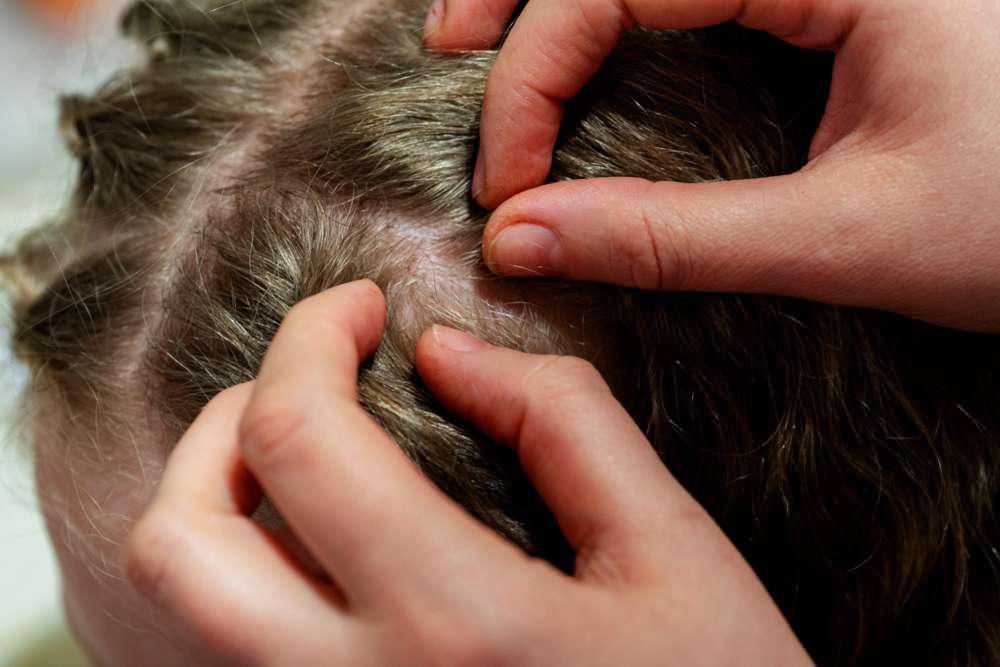
Dry, Itchy Skin? Learn the Signs of Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is a common chronic skin condition that can cause persistent dryness, itching, and irritation. Although it often starts in childhood, many adults also experience ongoing symptoms. Understanding the potential causes, common triggers, and how to manage flare-ups can make a real difference in daily comfort. Whether you or someone you care about is living with this condition, staying informed is the first step to effective care.
What exactly is atopic dermatitis?
Atopic dermatitis, also known as eczema, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. It’s part of a group of allergic conditions that include asthma and hay fever. This condition affects the skin’s ability to retain moisture and protect against irritants and allergens. People with atopic dermatitis often experience periods of flare-ups followed by periods of remission, making it a challenging condition to manage long-term.
How do symptoms differ between adults and children?
While atopic dermatitis can affect people of all ages, its presentation can vary between adults and children. In infants and young children, the condition often appears as red, itchy patches on the face, scalp, and outer surfaces of the arms and legs. As children grow older, the rash may become more prominent in the creases of elbows and knees, as well as on the neck, wrists, and ankles.
In adults, atopic dermatitis tends to be more localized and chronic. Common areas affected include the face, neck, hands, and feet. Adults may also experience more intense itching and dryness compared to children. Additionally, adult-onset atopic dermatitis can be more persistent and resistant to treatment, often requiring a comprehensive management approach.
What are the common triggers for atopic dermatitis flare-ups?
Identifying and avoiding triggers is crucial for managing atopic dermatitis. Common triggers include:
-
Environmental factors: Dry air, extreme temperatures, and high humidity can all exacerbate symptoms.
-
Allergens: Dust mites, pet dander, pollen, and certain foods can trigger flare-ups in some individuals.
-
Irritants: Harsh soaps, detergents, fragrances, and certain fabrics (like wool) can irritate sensitive skin.
-
Stress: Emotional stress can worsen symptoms or trigger flare-ups.
-
Hormonal changes: Some women may experience flare-ups related to their menstrual cycle or during pregnancy.
-
Infections: Bacterial or viral infections can sometimes trigger or worsen atopic dermatitis.
How is atopic dermatitis diagnosed and treated?
Diagnosing atopic dermatitis typically involves a thorough physical examination and review of medical history. In some cases, allergy tests or skin biopsies may be performed to rule out other conditions. There’s no single test to definitively diagnose atopic dermatitis, so healthcare providers rely on a combination of symptoms, family history, and physical findings.
Treatment for atopic dermatitis is multifaceted and often involves a combination of approaches:
-
Moisturizing: Regular use of emollients helps maintain skin hydration and barrier function.
-
Topical medications: Corticosteroid creams or ointments can reduce inflammation and itching during flare-ups.
-
Immunomodulators: Non-steroidal topical medications like tacrolimus or pimecrolimus can help manage symptoms.
-
Systemic medications: In severe cases, oral medications or injectable biologics may be prescribed.
-
Phototherapy: Controlled exposure to ultraviolet light can help reduce inflammation in some cases.
-
Lifestyle changes: Identifying and avoiding triggers, using gentle skincare products, and managing stress can all contribute to better symptom control.
What are some unique facts about atopic dermatitis in the USA?
Atopic dermatitis affects millions of Americans, with prevalence rates increasing over the past few decades. Interestingly, studies have shown that the condition is more common in urban areas compared to rural regions in the United States. This urban-rural difference may be due to factors such as air pollution, dietary habits, or differences in exposure to allergens and microbes during early childhood.
Additionally, research indicates that atopic dermatitis disproportionately affects certain ethnic groups in the USA. African American and Asian American children tend to have higher rates of the condition compared to Caucasian children. This disparity highlights the need for culturally competent care and targeted education efforts to address the unique challenges faced by different communities.
What are the latest advancements in atopic dermatitis treatment?
Recent years have seen significant advancements in the treatment of atopic dermatitis, particularly for moderate to severe cases that don’t respond well to traditional therapies.
| Treatment | Type | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Dupilumab | Injectable biologic | Targets specific immune pathways, effective for moderate to severe cases |
| Crisaborole | Topical PDE4 inhibitor | Non-steroidal option for mild to moderate atopic dermatitis |
| JAK inhibitors | Oral medication | Emerging class of drugs showing promise for severe cases |
| Microbiome-based therapies | Topical treatments | Aim to restore balance of skin microbiome |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
These new treatments offer hope for individuals who have struggled with conventional therapies, potentially improving quality of life and reducing the burden of this chronic condition.
In conclusion, atopic dermatitis is a complex, chronic skin condition that requires a comprehensive approach to management. By understanding the nature of the condition, identifying personal triggers, and working closely with healthcare providers, individuals with atopic dermatitis can develop effective strategies to minimize flare-ups and maintain healthier skin.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.