Understanding the Risks: Why Seniors Shouldn’t Ignore Atopic Dermatitis Symptoms
Atopic Dermatitis, or eczema, can present unique challenges for seniors. Identifying and managing its symptoms early is essential to avoid discomfort and possible complications. Seeking timely treatment can help improve daily life and reduce flare-ups over time.
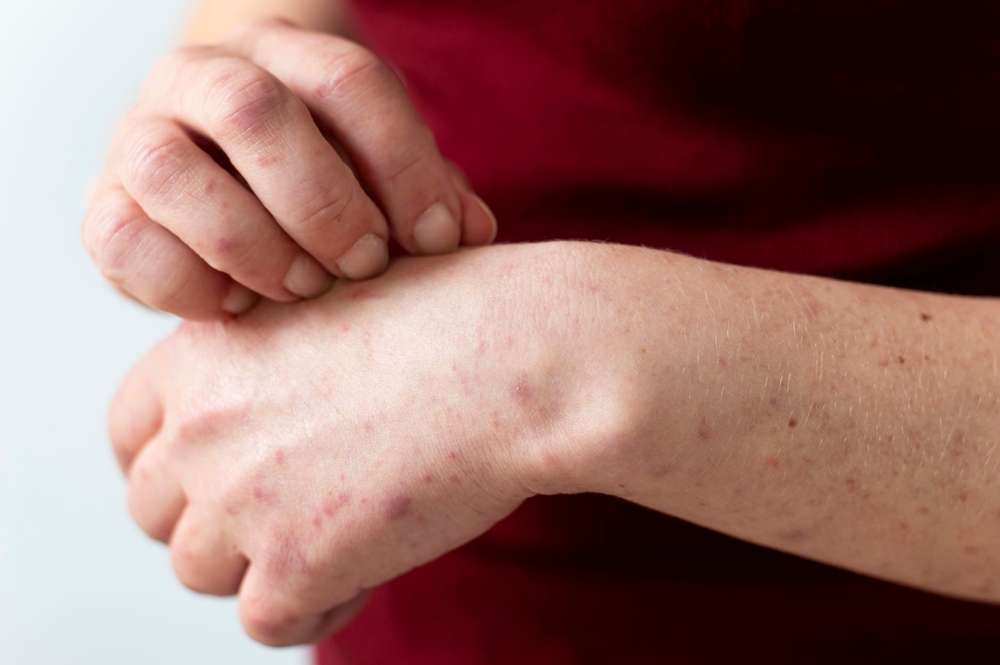
How does atopic dermatitis differ in seniors?
Atopic dermatitis in seniors often presents differently than in younger individuals. As we age, our skin becomes thinner, drier, and less elastic, making it more susceptible to irritation and inflammation. In older adults, atopic dermatitis may appear as dry, scaly patches on the skin, particularly in areas like the hands, face, and neck. The itching associated with the condition can be more intense in seniors, leading to a higher risk of skin damage from scratching.
Additionally, seniors may experience more widespread inflammation and slower healing times compared to younger individuals. This can make managing the condition more challenging and increase the risk of complications if left untreated.
What are the common triggers for atopic dermatitis in older adults?
Understanding the triggers of atopic dermatitis is essential for effective management, especially in seniors. Common triggers for older adults include:
-
Environmental factors: Extreme temperatures, low humidity, and exposure to irritants like harsh soaps or detergents can exacerbate symptoms.
-
Stress: Emotional stress can trigger flare-ups, which may be more common in seniors dealing with life changes or health issues.
-
Allergens: Dust mites, pet dander, and certain foods can trigger atopic dermatitis in sensitive individuals.
-
Medications: Some medications commonly prescribed to seniors may cause skin dryness or irritation, potentially triggering atopic dermatitis symptoms.
-
Hormonal changes: Age-related hormonal shifts can affect skin health and potentially worsen atopic dermatitis symptoms.
Identifying and avoiding these triggers can help seniors better manage their condition and reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups.
How can inflammation be effectively reduced in seniors with atopic dermatitis?
Reducing inflammation is crucial for managing atopic dermatitis in seniors. Several approaches can be effective:
-
Moisturizing: Regular use of fragrance-free, hypoallergenic moisturizers can help maintain skin hydration and reduce inflammation.
-
Topical corticosteroids: These prescription medications can help reduce inflammation and itching during flare-ups. However, long-term use should be monitored by a healthcare professional due to potential side effects.
-
Non-steroidal topical treatments: Medications like tacrolimus or pimecrolimus can help manage inflammation without the potential side effects of steroids.
-
Oral medications: In severe cases, oral antihistamines or immunosuppressants may be prescribed to control inflammation and itching.
-
Light therapy: Controlled exposure to UVB light under medical supervision can help reduce inflammation in some cases.
It’s important for seniors to work closely with their healthcare providers to develop an appropriate treatment plan that addresses their specific needs and considers any other health conditions they may have.
Why is preventing skin infections crucial for seniors with atopic dermatitis?
Seniors with atopic dermatitis have an increased risk of developing skin infections due to the compromised skin barrier and frequent scratching. Preventing these infections is crucial for several reasons:
-
Weakened immune system: As we age, our immune system becomes less effective, making it harder to fight off infections.
-
Slower healing: Seniors often experience slower wound healing, which can prolong the recovery from skin infections.
-
Complications: Skin infections in seniors can lead to more severe complications, such as cellulitis or sepsis, which can be life-threatening.
-
Quality of life: Recurring infections can significantly impact a senior’s quality of life, leading to discomfort, social isolation, and decreased mobility.
To prevent skin infections, seniors should maintain good hygiene practices, avoid scratching, keep nails short and clean, and promptly treat any cuts or abrasions. Regular check-ups with a dermatologist can also help identify and address potential infection risks early.
What are the latest treatment options for managing atopic dermatitis in seniors?
Recent advancements in atopic dermatitis treatment offer new hope for seniors struggling with the condition. Some of the latest treatment options include:
-
Biologics: Injectable medications like dupilumab target specific components of the immune system to reduce inflammation and itching.
-
JAK inhibitors: Oral medications such as upadacitinib and abrocitinib work by blocking certain enzymes involved in the inflammatory response.
-
Microbiome-based therapies: Emerging treatments aim to restore the balance of beneficial bacteria on the skin to improve barrier function and reduce inflammation.
-
Advanced moisturizers: New formulations containing ceramides, hyaluronic acid, and other skin-supporting ingredients can help improve skin hydration and barrier function.
-
Personalized treatment plans: Advancements in genetic testing and biomarker analysis allow for more tailored treatment approaches based on an individual’s specific skin characteristics and immune responses.
While these new treatments offer promising results, it’s essential for seniors to consult with their healthcare providers to determine the most appropriate and safe options for their individual cases.
In conclusion, atopic dermatitis in seniors is a complex condition that requires careful attention and management. By understanding the unique challenges faced by older adults with this condition, recognizing common triggers, and staying informed about the latest treatment options, seniors can take proactive steps to improve their skin health and overall quality of life. Early intervention and consistent care are key to preventing complications and maintaining healthy, comfortable skin throughout the golden years.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.