Understanding Hypersomnia: Causes of Excessive Daytime Sleepiness and Hidden Symptoms to Watch
Feeling overwhelmingly tired during the day — even after a full night’s sleep — could be more than just fatigue. It might be a sign of hypersomnia, a chronic sleep disorder often misunderstood or misdiagnosed. By learning to recognize its hidden symptoms and root causes, individuals can take the first step toward effective treatment and improved daily functioning.
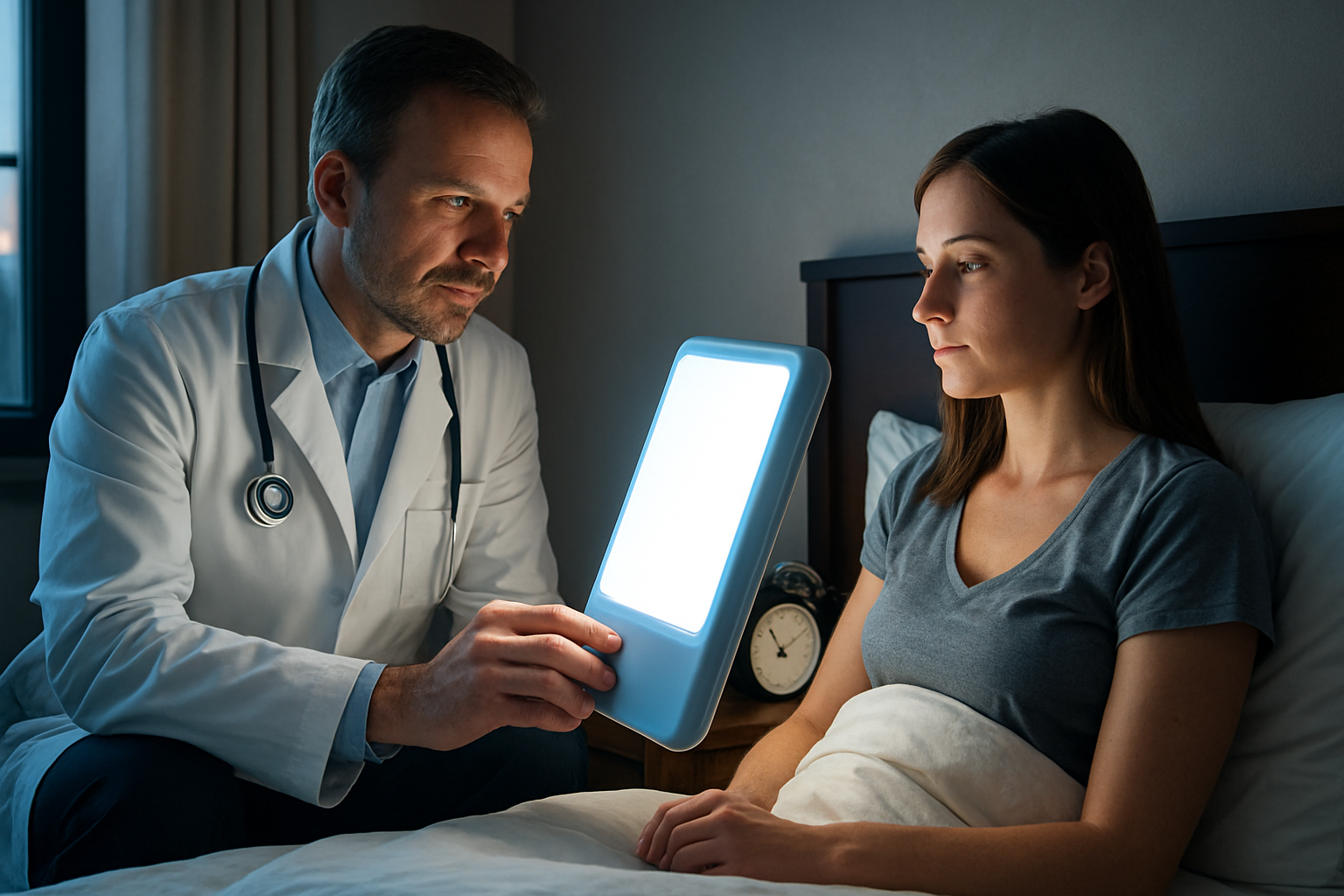

What is hypersomnia and how does it differ from regular tiredness?
Hypersomnia is a neurological disorder characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS) that persists even with adequate or prolonged nighttime sleep. Unlike regular tiredness, which can be resolved with proper rest, hypersomnia is a chronic condition that significantly impacts daily life. Many sufferers mistake hypersomnia for regular tiredness, delaying proper diagnosis and treatment. This misconception often leads to prolonged suffering and potential complications in various aspects of life.
What are the hidden symptoms of hypersomnia beyond excessive sleepiness?
While excessive daytime sleepiness is the primary symptom of hypersomnia, there are several hidden symptoms that individuals and healthcare providers should be aware of. These include memory lapses, irritability, and poor concentration. People with hypersomnia may also experience difficulty waking up in the morning, feeling disoriented upon awakening (sleep drunkenness), and a constant need for naps that don’t provide relief. These symptoms can significantly impact personal relationships, work performance, and overall quality of life.
What are the main causes of hypersomnia?
Hypersomnia can have various causes, ranging from neurological conditions to lifestyle factors. Some common causes include:
-
Narcolepsy: A neurological disorder affecting the brain’s ability to regulate sleep-wake cycles.
-
Idiopathic hypersomnia: A condition where the cause is unknown.
-
Sleep apnea: A disorder characterized by repeated pauses in breathing during sleep.
-
Certain medications: Some antidepressants, antihistamines, or pain medications can cause drowsiness.
-
Medical conditions: Such as hypothyroidism, depression, or chronic fatigue syndrome.
-
Substance abuse: Alcohol or drug use can disrupt sleep patterns and lead to hypersomnia.
Understanding the underlying cause is crucial for effective treatment and management of hypersomnia.
How are sleep studies used to diagnose hypersomnia?
Sleep studies play a vital role in diagnosing hypersomnia and identifying potential underlying causes. These studies can reveal disruptions not obvious in nightly sleep patterns, providing valuable insights for healthcare providers. The most common sleep studies used in hypersomnia diagnosis include:
-
Polysomnography (PSG): An overnight test that monitors brain activity, eye movements, muscle activity, and other bodily functions during sleep.
-
Multiple Sleep Latency Test (MSLT): A daytime test that measures how quickly a person falls asleep in a quiet environment.
-
Actigraphy: A non-invasive test that uses a wrist-worn device to track sleep-wake patterns over an extended period.
These tests help differentiate hypersomnia from other sleep disorders and guide treatment decisions.
What are the potential consequences of untreated hypersomnia?
Untreated hypersomnia can have far-reaching effects on an individual’s life. It may affect work performance, leading to decreased productivity, errors, or even job loss. Personal relationships can suffer due to irritability, lack of energy for social activities, or misunderstandings about the condition. Academic performance may decline in students with hypersomnia. There’s also an increased risk of accidents, particularly while driving or operating machinery, due to excessive sleepiness. Long-term untreated hypersomnia may contribute to mental health issues such as depression and anxiety, further impacting overall well-being.
What are the latest treatment options for hypersomnia?
New treatment options help restore energy levels and support healthier sleep cycles for individuals with hypersomnia. These may include:
-
Stimulant medications: Such as modafinil or methylphenidate to promote wakefulness.
-
Sodium oxybate: A medication that helps improve nighttime sleep quality and reduce daytime sleepiness.
-
Antidepressants: Certain types may be prescribed to help regulate sleep patterns.
-
Behavioral therapies: Including cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I) to improve sleep habits.
-
Lifestyle modifications: Such as maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, avoiding alcohol and caffeine, and regular exercise.
| Treatment Option | Purpose | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Modafinil | Promotes wakefulness | Headache, nausea, anxiety |
| Sodium oxybate | Improves nighttime sleep | Dizziness, bedwetting, sleepwalking |
| Venlafaxine (antidepressant) | Regulates sleep patterns | Nausea, dry mouth, insomnia |
| CBT-I | Improves sleep habits | None (non-pharmacological) |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
The choice of treatment depends on the underlying cause of hypersomnia, the severity of symptoms, and individual patient factors. A sleep specialist can help determine the most appropriate treatment plan, which may involve a combination of approaches for optimal results.
In conclusion, hypersomnia is a complex sleep disorder that goes beyond mere tiredness. Recognizing its hidden symptoms, understanding its causes, and seeking proper diagnosis through sleep studies are crucial steps toward effective management. With advancements in treatment options, individuals with hypersomnia can find relief and improve their quality of life. If you suspect you may have hypersomnia, consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and personalized treatment recommendations.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.