HOW PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS SHOWS UP IN OLDER ADULTS – LEARN THE SYMPTOMS
Psoriatic arthritis can affect older adults in subtle yet serious ways. Joint pain, stiffness, and skin changes may seem like normal aging—but they could be signs of something more. Discover how this condition presents in seniors and what symptoms to watch for before it progresses.
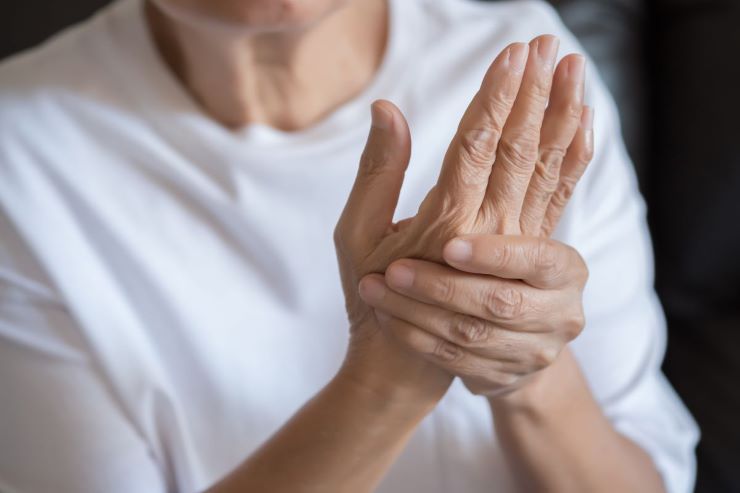

What is psoriatic arthritis and how does it differ in seniors?
Psoriatic arthritis is an inflammatory condition that affects some people with psoriasis, causing joint pain, stiffness, and swelling. In seniors, the disease can be more challenging to diagnose due to its similarity with other age-related joint issues. Older adults may experience a slower onset of symptoms compared to younger patients, making it easier to dismiss early warning signs as part of normal aging.
The condition in seniors often affects larger joints like knees and hips, as opposed to the smaller joints typically impacted in younger individuals. Additionally, older adults with psoriatic arthritis may have less severe skin involvement, further complicating diagnosis. The immune system changes that come with aging can also influence how the disease presents and progresses in this population.
What are the early signs of psoriatic arthritis in older adults?
Recognizing the early signs of psoriatic arthritis in seniors is crucial for timely intervention. Some key indicators include:
-
Joint pain and stiffness, especially in the morning or after periods of inactivity
-
Swelling in one or more joints, often asymmetrically
-
Changes in nail appearance, such as pitting or separation from the nail bed
-
Fatigue and reduced energy levels
-
Mild skin rashes or patches, which may be less prominent than in younger patients
-
Tenderness or pain in areas where tendons attach to bones, like the heel or elbow
It’s important to note that these symptoms can develop gradually and may be attributed to other conditions common in older adults. Regular check-ups and open communication with healthcare providers are essential for accurate diagnosis.
How does psoriatic arthritis affect the quality of life in seniors?
Psoriatic arthritis can significantly impact the quality of life for older adults. The chronic pain and stiffness associated with the condition can limit mobility and independence, making daily activities more challenging. Seniors may find it difficult to perform tasks like dressing, cooking, or maintaining personal hygiene without assistance.
The fatigue that often accompanies psoriatic arthritis can lead to decreased social engagement and physical activity, potentially exacerbating other health issues common in older age. Moreover, the visible skin changes may cause emotional distress and affect self-esteem, leading to social isolation or depression.
Sleep disturbances are also common, as joint pain can make it difficult to find comfortable sleeping positions. This can result in a cycle of poor sleep, increased pain, and further reduced quality of life. Managing psoriatic arthritis in seniors often requires a multidisciplinary approach to address both physical symptoms and emotional well-being.
What is the hidden link between psoriasis and arthritis in older adults?
The connection between psoriasis and arthritis in older adults is not always obvious, as skin symptoms may be less severe or even absent in some cases. This “hidden link” lies in the shared inflammatory processes that underlie both conditions. In seniors, long-standing psoriasis may eventually lead to joint involvement, even if skin symptoms have been mild or well-controlled.
The immune system dysfunction that causes psoriasis can also trigger inflammation in the joints, leading to arthritis. This link is particularly important in older adults, as they may have had psoriasis for many years before developing joint symptoms. Understanding this connection can help healthcare providers identify at-risk patients and monitor them for early signs of psoriatic arthritis.
How can seniors manage psoriatic arthritis symptoms effectively?
Managing psoriatic arthritis in seniors requires a comprehensive approach tailored to their specific needs and overall health status. Some effective strategies include:
-
Medications: Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) and biologics can help control inflammation and slow disease progression. NSAIDs may provide pain relief but should be used cautiously due to potential side effects in older adults.
-
Physical therapy: Gentle exercises and stretches can help maintain joint flexibility and muscle strength. A physical therapist can design a safe, effective program for seniors.
-
Lifestyle modifications: Weight management, smoking cessation, and a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can help reduce symptoms and improve overall health.
-
Assistive devices: Tools like jar openers, ergonomic utensils, and mobility aids can help seniors maintain independence and perform daily tasks with less pain.
-
Stress management: Techniques such as meditation, yoga, or tai chi can help reduce stress and improve overall well-being.
Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers are essential to monitor disease progression and adjust treatment plans as needed. Seniors should also be educated about the importance of medication adherence and potential drug interactions with other medications they may be taking for age-related conditions.
What treatment options are available for psoriatic arthritis in older adults?
Treatment options for psoriatic arthritis in older adults must balance efficacy with safety considerations unique to this age group. The following table outlines common treatment approaches:
| Treatment Type | Examples | Benefits | Considerations for Seniors |
|---|---|---|---|
| NSAIDs | Ibuprofen, naproxen | Pain relief, reduced inflammation | Higher risk of gastrointestinal and cardiovascular side effects |
| DMARDs | Methotrexate, sulfasalazine | Slows disease progression | May require dose adjustments, increased risk of infections |
| Biologics | TNF inhibitors, IL-17 inhibitors | Targeted immune system modulation | Careful monitoring for infections, potential cardiovascular risks |
| Topical treatments | Corticosteroid creams, vitamin D analogs | Manages skin symptoms | Less systemic side effects, but may have limited efficacy for joint symptoms |
| Physical therapy | Tailored exercise programs | Improves mobility and strength | Must be adapted to individual capabilities and limitations |
| Occupational therapy | Joint protection techniques, assistive devices | Enhances daily functioning | Focuses on maintaining independence and quality of life |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
In conclusion, recognizing how psoriatic arthritis presents in older adults is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management. While the symptoms may be subtle or easily confused with normal aging, understanding the unique aspects of this condition in seniors can lead to better outcomes and improved quality of life. With proper care and a comprehensive treatment approach, older adults with psoriatic arthritis can maintain their independence and well-being.